Did you know that the types of curriculum used in different schools can greatly impact students' academic success and personal growth?
In fact, research has shown that a well-designed curriculum can boost student engagement and achievement.
Understanding the curriculum meaning and it’s types is essential for teachers who want to make their lessons more effective and meaningful.
Whether you’re an experienced curriculum expert or a classroom teacher, understanding the meaning of curriculum and the different types of curriculum is key to great teaching.
In this blog we’ll cover:
- What is Curriculum
- Importance of Curriculum in Teaching
- What are the 10 Types of Curriculum?
- Comparison Table for Different Types of Curriculum
- Tips for Effective Curriculum Planning
- BONUS: Do’s and Dont's of Curriculum Planning
Curriculum refers to the lessons and academic content taught in a school or in a specific course or program. It encompasses the knowledge, skills, attitudes, and values that students are expected to learn.
Understanding the curriculum meaning helps educators design effective and meaningful lessons.
Think of the curriculum as a roadmap for learning that guides both teachers and students through the educational journey.
At its core, a curriculum outlines what students need to know and be able to do at each grade level or stage of their education.
It includes:
- Goals and Objectives: What students should achieve by the end of the course or grade level.
- Content: The specific information and skills that will be taught.
- Instructional Methods: The way teachers will deliver the content and engage students in learning.
- Assessment: The tools and methods used to evaluate whether students have met the learning goals, like quizzes, tests, projects, and presentations.
- Resources: The materials and tools, such as textbooks, digital content, and hands-on activities, that support learning.
Different schools and educational systems may have their own unique curricula, tailored to meet the needs and interests of their students.
For example, some schools might focus more on science and technology, while others might emphasize the arts or social studies.
By following a structured curriculum, schools can ensure that students build on their knowledge year after year, preparing them for future academic success and life beyond the classroom.
Let’s look at a sample curriculum to understand the meaning of curriculum more comprehensively.
Sample Curriculum
Here is a sample image of how a curriculum looks like to help you understand it better.
A well-designed curriculum helps ensure that all students have access to a high-quality education. Understanding the different types of curriculum in education allows educators to tailor their teaching strategies to meet diverse learning needs.
It provides a clear framework for what should be taught and learned, helping teachers plan their lessons and giving students a clear understanding of what is expected of them.
Now that we understand what is curriculum, let's explore why having a well-structured curriculum is so crucial for effective teaching and learning.
A well-structured curriculum is essential for delivering quality education. Here's why a good curriculum matters for you as a teacher:
1. Guides Teaching and Learning
A curriculum serves as your guide, helping you plan lessons and teach effectively. It outlines what your students need to learn and the best ways to teach those concepts.
It ensures you cover all necessary topics and skills in a logical sequence, building on previous knowledge and preparing your students for future learning.
2. Ensures Consistency
A structured curriculum ensures that all your students receive the same quality of education, regardless of their classroom or school.
It helps maintain consistency across different classrooms and schools, making sure all students achieve the same learning goals and standards.
3. Sets Clear Goals and Expectations
A curriculum sets clear learning goals and expectations for your students. This helps them understand what they need to know and be able to do by the end of each grade or course.
It provides a roadmap for your students to follow, giving them a sense of direction and purpose in their studies.
4. Supports Teacher Preparation
With a well-defined curriculum, you have a clear plan to follow, which helps you prepare your lessons more efficiently.
It provides resources and materials that you can use to enhance your teaching, such as textbooks, lesson plans, and instructional tools.
5. Facilitates Assessment and Evaluation
A curriculum includes assessment methods and tools that help you evaluate student progress and understanding.
It allows you to identify areas where students may need additional support and adjust your teaching strategies accordingly.
6. Promotes Student Engagement
A thoughtfully designed curriculum includes a variety of activities and teaching methods to engage your students in learning.
It caters to different learning styles and interests, making learning more enjoyable and effective for all students.
7. Addresses Diverse Need
A comprehensive curriculum takes into account the diverse needs of your students, including those with different abilities, backgrounds, and learning preferences.
It includes differentiated instruction and support strategies to ensure that all students have the opportunity to succeed.
8. Prepares Students for the Future
A curriculum is designed to equip your students with the knowledge and skills they need to succeed in future academic pursuits and in life beyond school.
It includes not only academic content but also important life skills, such as critical thinking, problem-solving, and collaboration.
In summary, a well-structured curriculum is the backbone of effective education.
Having discussed the importance of a well-structured curriculum, let's delve into the various types of curriculum and how each plays a unique role in the educational journey.
The right curriculum can help students gain knowledge efficiently. Let’s take a look at some of the popular curriculum types that are in use:
1. Written Curriculum 📘
The written curriculum, also known as the explicit or overt curriculum, is the formal and documented curriculum designed by educational experts and authorities. It includes specific subjects, content, learning objectives, and instructional strategies that teachers are expected to follow in the classroom.
Benefits of Having a Written Curriculum:
- Clarity for You and Your Students: Having a written curriculum means everyone—you, students, and parents—knows exactly what's on the learning agenda. It helps you plan lessons that hit the mark.
- Quality of Educational Content: It's like having a blueprint for great teaching. By setting clear goals and standards, you can focus on delivering engaging lessons that really help students learn.
- Consistency Across Classrooms: When everyone follows the same curriculum, it ensures that every student gets a fair shot at a solid education. It keeps things fair and makes sure your efforts in the classroom pay off for everyone.
2. Hidden Curriculum 🕵️
The hidden curriculum consists of the lessons, values, and perspectives that students learn indirectly through the school culture, environment, and social interactions. These are not explicitly included in the formal written curriculum but significantly impact students' development and behavior.
Benefits of Understanding the Hidden Curriculum:
- Fosters Holistic Development: The hidden curriculum helps you recognize the broader social and emotional lessons your students are learning. This awareness allows you to guide them in developing important life skills, such as empathy, teamwork, and resilience.
- Improves School Culture: By acknowledging and addressing the hidden curriculum, you can contribute to a positive school culture where values like respect, responsibility, and inclusivity are promoted.
- Enhances Teaching Effectiveness: Understanding the hidden curriculum can help you better connect with your students and address their needs beyond academics. This can lead to a more supportive and engaging learning environment.
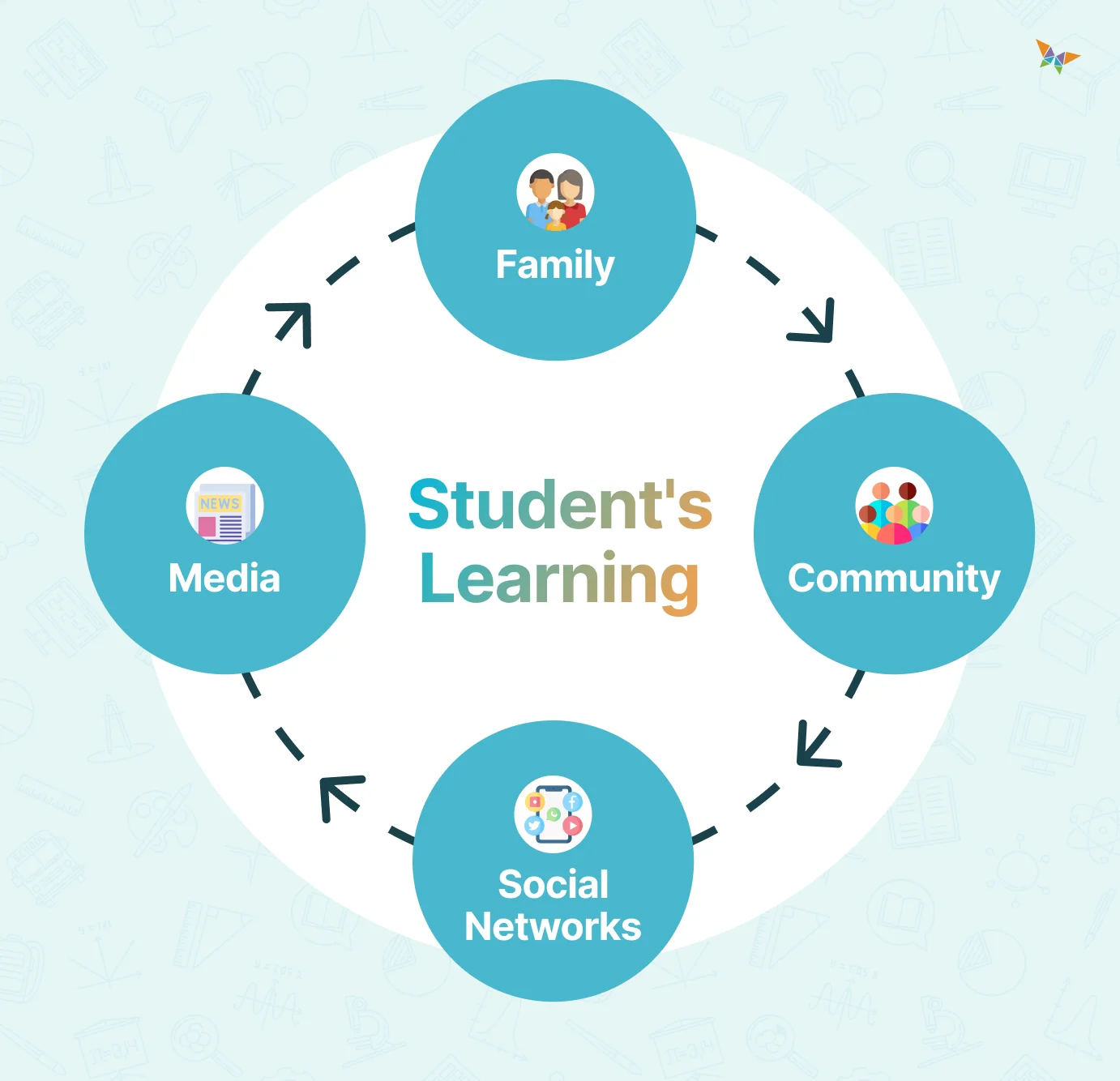
3. Societal Curriculum 🌍
Societal curriculum refers to the lessons and knowledge that students acquire from their interactions with society outside of the formal school environment. This includes influences from family, media, community, and social networks.
Benefits of Recognizing Societal Curriculum:
- Broader Perspective: By acknowledging the societal curriculum, you can help your students make connections between their school learning and real-world experiences, enhancing their overall understanding.
- Enhanced Relevance: Incorporating societal curriculum elements into your teaching makes learning more relevant and engaging for students, as they see the practical applications of what they learn in school.
- Support for Diverse Learning: Understanding the societal curriculum helps you address the diverse backgrounds and experiences of your students, fostering a more inclusive and supportive classroom environment.
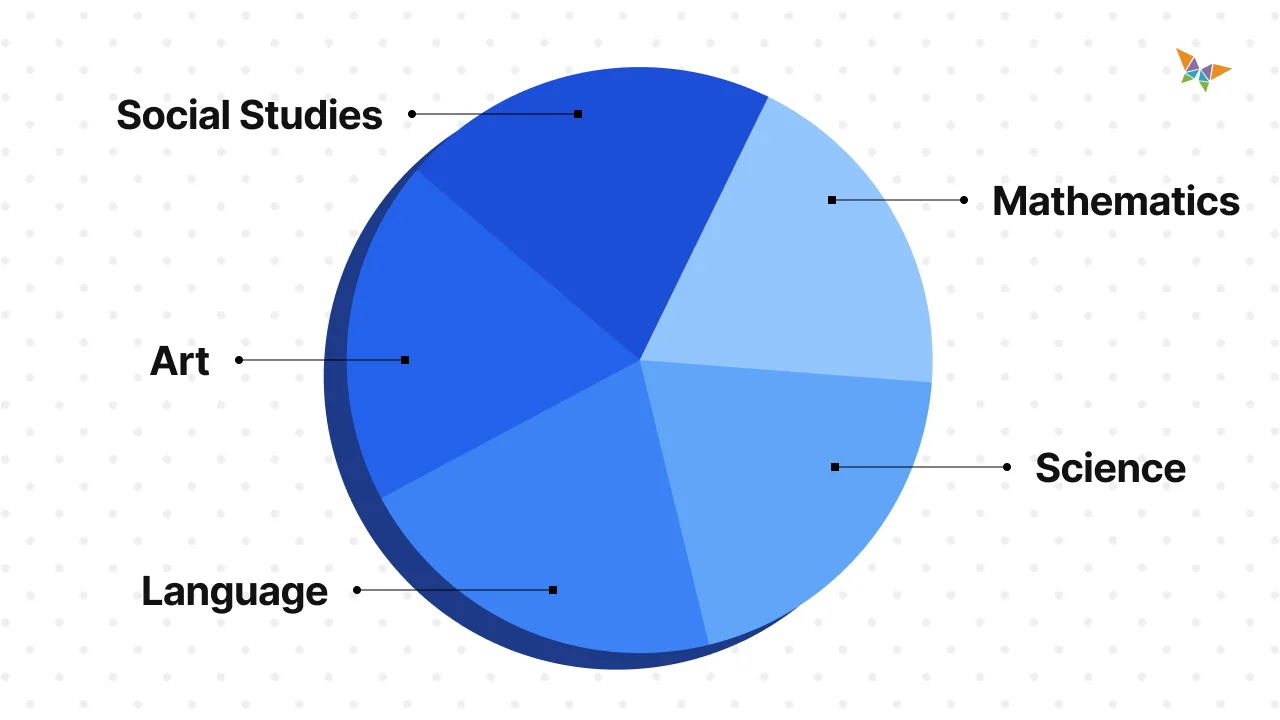
4. Subject-Centered Curriculum 📚
A subject-centered curriculum is focused on specific subjects or disciplines, with the primary goal of deepening students' knowledge and understanding of those subjects. This type of curriculum is often structured around a series of topics and skills within a particular subject area.
Benefits of a Subject-Centered Curriculum:
- Depth of Knowledge: This curriculum allows you to focus deeply on a particular subject, helping your students develop a strong foundation and expertise in that area.
- Structured Learning: With clear topics and skills to cover, you can create a structured learning path that builds on previous knowledge and prepares students for more advanced study.
- Specialized Instruction: It enables you to use subject-specific teaching methods and resources, making your instruction more effective and engaging for students.
5. Student-Centered Curriculum 👩🎓
A student-centered curriculum is designed to focus on the needs, interests, and learning styles of individual students. It emphasizes active learning and student engagement, giving students more control over their learning process.
Benefits of a Student-Centered Curriculum:
- Personalized Learning: This curriculum allows you to tailor your teaching to meet the unique needs and interests of each student, enhancing their motivation and engagement.
- Active Participation: By involving students in their own learning process, you can foster critical thinking, problem-solving skills, and independence.
- Flexible and Adaptive: It provides flexibility for you to adjust your teaching strategies based on students' progress and feedback, ensuring that learning remains dynamic and effective.
6. Activity-Centered Curriculum 🎨
An activity-centered curriculum is designed around engaging students in hands-on activities and experiences. This type of curriculum emphasizes learning through doing, encouraging students to apply their knowledge in practical and creative ways.
Benefits of an Activity-Centered Curriculum:
- Engaged Learning: By involving students in interactive and practical activities, you can make learning more engaging and enjoyable for them.
- Better Retention: Hands-on activities help students retain information better as they actively apply what they have learned.
- Skill Development: It promotes the development of important skills such as teamwork, creativity, and problem-solving, preparing students for real-world challenges.
7. Teacher-Centered Curriculum 🧑🏫
In a teacher-centered curriculum, the teacher is the primary authority and decision-maker in the classroom. This type of curriculum emphasizes direct instruction, where the teacher delivers content and students passively receive information.
Benefits of a Teacher-Centered Curriculum:
- Structured Environment: Provides a clear and structured learning environment, ensuring that all necessary content is covered systematically.
- Efficient Content Delivery: Allows you to efficiently deliver a large amount of information within a set time frame, maintaining control over the pace and direction of the lesson.
- Consistency: Ensures consistency in instruction, as you follow a predetermined curriculum and teaching methods.
8. Integrated Curriculum 🔗
An integrated curriculum connects multiple subjects and disciplines into a cohesive learning experience. This approach helps students see the relationships between different areas of knowledge and apply their learning in a more holistic way.
Benefits of an Integrated Curriculum:
- Holistic Learning: Encourages students to make connections between different subjects, fostering a deeper understanding and appreciation of the material.
- Real-World Relevance: Helps students see the practical applications of their learning, making education more relevant to their lives and future careers.
- Enhanced Critical Thinking: Promotes critical thinking and problem-solving skills as students learn to integrate and apply knowledge from various disciplines.
9. Core Curriculum 📖
A core curriculum includes the essential subjects and skills that all students are required to learn. It is designed to provide a solid foundation of knowledge and prepare students for further education and life beyond school.
Benefits of a Core Curriculum:
- Essential Knowledge: Ensures that all students acquire a basic foundation of essential knowledge and skills, regardless of their background or future plans.
- Consistency: Provides a consistent and equitable education for all students, setting a common standard for learning.
- Preparation for the Future: Prepares students for further education, careers, and responsible citizenship by focusing on fundamental subjects and skills.
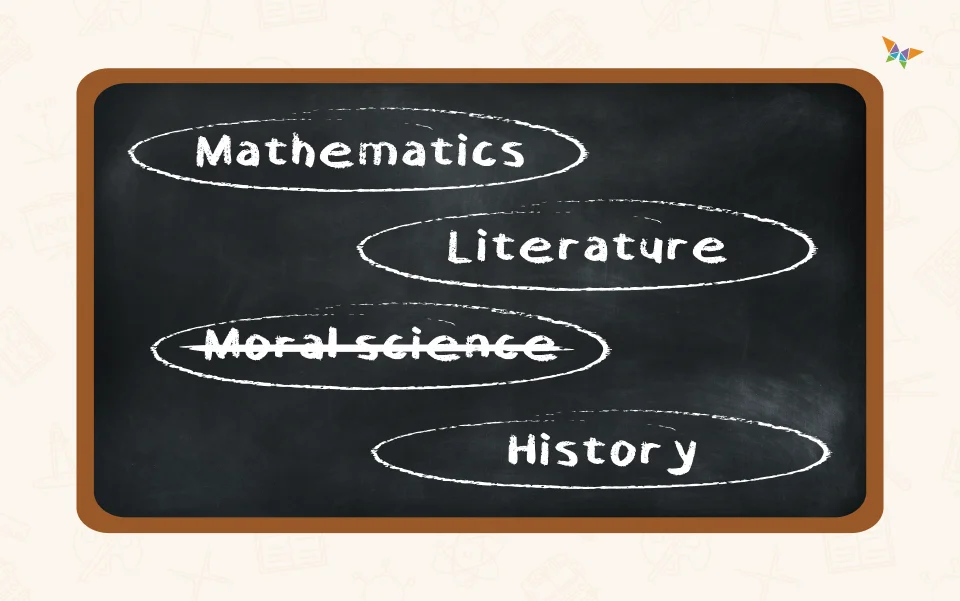
10. Null Curriculum❌
Null curriculum refers to the topics, subjects, and content that are deliberately excluded from the formal curriculum. These omissions can reflect educational priorities, societal values, or practical constraints.
Benefits of Recognizing the Null Curriculum:
- Awareness of Bias: Helps you understand and address potential biases and gaps in the curriculum, ensuring a more balanced and inclusive education.
- Curriculum Improvement: By identifying what is omitted, you can work towards filling these gaps and providing a more comprehensive educational experience for your students.
- Critical Thinking: Encourages students to think critically about what they are learning and question why certain topics are included or excluded from their education.
Understanding these different types of curriculum can help you choose the best methods to meet your students' needs and achieve educational goals effectively.
Each type offers unique strengths and can be adapted to various educational contexts.
Now that we've explored the different types of curriculum, let's compare them side by side to better understand their unique characteristics and applications.
Here's a simplified comparison table for different types of curriculum:
Now that we've compared the different types of curriculum, let's explore some tips for effective curriculum planning to help you implement these strategies successfully.
Planning a curriculum can be a challenging task, but with the right strategies and mindset, you can create a comprehensive and effective plan that enhances student learning. Here are some bonus tips to help you succeed:
1. Understand Your Students and Set Clear Expectations
Get to know your students—what they enjoy learning and how they learn best, whether it's through experiments, stories, or hands-on activities.
For example, if you have a class that loves science experiments, incorporate more hands-on activities into your lessons.
This understanding helps you design lessons that engage them. Then, set clear goals and expectations for each lesson.
It helps them see where they're headed and how to get there. Break down your learning goals in simple, understandable terms. For instance, instead of saying "We'll explore photosynthesis," say "We'll learn how plants make their food from sunlight."
2. Be Flexible and Gather Feedback
Be prepared to adjust your curriculum based on student feedback and performance. If an activity isn't working, don't be afraid to tweak it.
Suppose you planned a group project, but students are struggling with teamwork. You might switch to smaller, paired activities.
Ask your students and colleagues for their opinions regularly. Maybe your students found a particular project boring, or your colleague has a fresh idea that could make a lesson more engaging. Flexibility and feedback are key to continuous improvement.
3. Integrate Technology
Use digital tools to make learning more interactive and fun.
For instance, use educational apps to create interactive quizzes or virtual whiteboards for collaborative projects.
Tools like Kahoot! can turn a regular quiz into an exciting game. Ensure your students develop digital literacy skills by integrating technology use into your lessons. This not only makes learning more engaging but also prepares them for the future.
4. Collaborate with Colleagues
Don't go it alone—share ideas and resources with your fellow teachers. Maybe another teacher has a fantastic lesson plan that you can adapt.
Consider co-teaching or planning interdisciplinary projects to provide a richer learning experience.
For example, team up with a history teacher to create a project that combines historical events with literature studies. Working together can lead to innovative curriculum ideas and a more cohesive learning environment.
5. Focus on Critical Thinking
Encourage your students to think deeply and ask questions. Design activities that require them to solve problems, analyze information, and make connections.
For example, you could create a project where students have to come up with solutions to a real-world problem, like designing an eco-friendly school.
This not only makes learning more relevant but also helps them develop essential critical thinking skills.
6. Assess and Reflect
Use a mix of assessments to understand how well your students are grasping the material. Regular quizzes, class discussions, and projects can give you insights into their progress.
Reflect on your teaching practices and curriculum effectiveness. What worked well? What could be improved?
For instance, after a unit on fractions, you might notice that some students are still struggling. This reflection helps you fine-tune your approach and better meet your students' needs.
7. Engage Families and the Community
Involve parents in the learning process. Share your curriculum plans with them and encourage them to support their children's learning at home.
For example, send home a newsletter with tips on how parents can help with homework. Utilize community resources like guest speakers, field trips, and local organizations to enrich your curriculum.
This not only broadens your students' learning experiences but also helps them connect classroom learning to the real world.
8. Plan for Differentiation
Not all students learn the same way or at the same pace. Design lessons that cater to different learning levels and styles.
Offer various activities and assignments that allow students to show their understanding in different ways.
For example, some students might write an essay, while others create a video presentation. Include strategies to support students with special needs, English language learners, and gifted students.
Differentiation ensures that all your students can succeed and feel valued.
By incorporating these tips into your curriculum planning process, you can create a dynamic and effective learning environment that supports student growth and achievement.
Remember, effective curriculum planning is an ongoing process that involves continuous learning, reflection, and adaptation.
Now that you have some valuable tips for effective curriculum planning, let's delve into the BONUS section: Do's and Don'ts of Curriculum Planning to ensure you're on the right track.
By following these do's and don'ts, you can create a more effective and responsive curriculum that meets the needs of all your students and enhances their learning experience.
The goal of this blog was to introduce you to the different types of curriculum and explain their impact on both you and your students.
We discussed various types of curriculum, such as written, hidden, societal, and more, and how each type involves teachers and students in different ways.
Each type of curriculum serves its own unique purpose, and you might choose to follow one or more depending on your specific needs.
Whether you're focusing on the written curriculum for structured learning or a societal curriculum for social skills, understanding the meaning and design of different types of curricula can help you select the best teaching style to meet your goals and enhance student learning effectively.
By grasping what is curriculum and the various types of curriculum design, you can better tailor your teaching strategies to support students' educational journeys.